laparoscopic gallbladder surgery
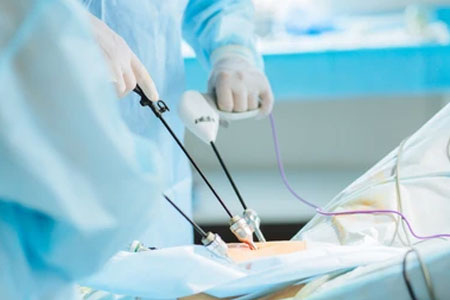
Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery, also known as laparoscopic cholecystectomy, is a minimally invasive procedure to remove the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ located beneath the liver that stores bile, a digestive fluid. This surgery is commonly performed to treat gallstones or gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis), which can cause pain, infection, or other complications.
When is Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery Needed?
- Gallstones: Hardened deposits of bile that can block the bile ducts, causing pain (biliary colic), infection, or inflammation.
- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by gallstones.
- Biliary Dyskinesia: A condition where the gallbladder does not function properly, leading to pain and digestive issues.
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, which can occur when a gallstone blocks the bile duct shared by the gallbladder and pancreas.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery:
- Minimally Invasive: Compared to open surgery, it involves smaller incisions, leading to less pain and scarring.
- Faster Recovery: Patients experience quicker recovery times and can return to normal activities sooner.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Less blood loss, lower risk of infection, and quicker healing.
Overall, laparoscopic gallbladder surgery is the preferred method for treating gallbladder problems due to its minimally invasive nature and quicker recovery time.
